
Certified Python Professional (C|PP™)
The CERTIFIED PYTHON PROFESSIONAL (C|PP™) is another labour of love for our team. We wanted to create something unique that would help all learners master Python programming in a short space of time, without the fuss and by example.
Following the same recipe as our successful Certified Blockchain Cryptocurrency Professional (C|BCP™), online self-study and self-paced course, our second major product was born. We built this course in the way we would have liked to have learnt Python, by example! We also took notes from our previous experiences and built a rich content course, full of examples at every stage of the course. Students who have feared learning a programming language, we have you covered! You will not regret taking our course and we look forward to working with you!
CERTIFIED PYTHON PROFESSIONAL
(C|PP™)
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language that was first created in the late 1980s by Guido van Rossum. It was named after the British comedy group Monty Python, as a nod to the creator's love of the group's work. Python was first released in 1991 and has since become one of the most popular programming languages in the world.
Python's popularity has grown over the years, in part because of its easy-to-learn syntax and its versatility. It is used in many fields, including web development, data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. In addition, Python is open source, which means that it can be freely distributed and modified. This has contributed to the growth of a large community of Python developers who contribute to the language's development.
One of the major benefits of Python is its ease of use. Its simple syntax and readability make it an ideal language for beginners to learn, but it is also powerful enough to be used by experienced programmers. Python's versatility also makes it an attractive language to use in a variety of fields, as mentioned earlier. It is particularly well-suited to data analysis and visualization, and many scientific and academic communities use Python in their research.
Python has had a significant impact on the world, particularly in the areas of scientific research, data analysis, and machine learning. Its ease of use has made it accessible to a wide range of users, from beginners to experienced developers, and its versatility has made it a popular language in many fields. Python has also contributed to the growth of a large community of developers who contribute to its development, and its open-source nature has made it accessible to all. Overall, Python has changed the world of programming in many ways and will continue to do so for years to come.
In the Certified Python Professional (C|PP™) course, we will teach you all you need to know about Python, working with everything Python can do, how to code, how it is implemented, how it influences the world and how it can be used in business and development projects.
CERTIFIED PYTHON PROFESSIONAL (C|PP™)

TARGET AUDIENCE
The following learners will benefit from the Certified Python Professional (C|PP™) course:
Beginners: Python's easy-to-learn syntax and high readability make it an ideal language for beginners who are just starting to learn programming.
Data scientists: Python is a popular language in the field of data science due to its ability to handle large datasets and its powerful libraries for data analysis and visualization.
Web developers: Python is commonly used in web development, particularly for back-end development, because of its simplicity and versatility.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning professionals: Python's powerful machine learning libraries, such as TensorFlow and Scikit-learn, make it a popular language for AI and ML applications.
Scientists and researchers: Python is widely used in scientific research because of its flexibility, large community of developers, and the ability to handle complex data.
Business analysts: Python's ease of use and powerful data analysis tools make it an ideal language for business analysts who need to work with large datasets and perform data analysis.
CURRICULUM
Learn everything you need to know about Python programming the future of the world all from one source!
5x days of intense, quality and fun learning.
Aesthetically pleasing in print, digital and audio formats.
Horizontal learning experience for more immersive study.
45+ Hours of learning rich, targeted and in-depth content without the fluff.
Content, demos, labs and exercises prepared by our professionals, at every stage and topic of the course for beginners and advanced levels.
Official and only learning courseware, for the C|PP™ Certification course and examination.
Courseware Formats:
Digital Courseware Book: for instructor-led courses (online or on-site) and for eLearning platform.
Print Courseware Book: for instructor-led courses (online or on-site) only.
Online Audiovisual Self-Study and Self-Paced course (via our Obi.Academy eLearning platform).
Course Delivery:
The Certified Python Professional™ - (C|PP™) course is available online as a self-paced self-study course or as an instructor-led online and onsite, with our approved training partners (ATPs) in the UK and Europe. Obipixel Ltd is actively in discussions with potential partners in the USA, Africa and Asia. To enquire about becoming an approved training provider and affiliate or a learner/attendee on our courses with our partners with Obi.Academy please contact us for further details.
Practical Project for Certification:
To attain the Certified Python Professional™ - (C|PP™) certification, students/attendees must complete their practical project in Module 9 of the course.
This will need to be marked and assessed by the Obipixel Ltd | OBI Academy team.
All code and documentation will be required for this process and every details will be given to students/attendees upon starting their course.
A practical project has been chosen to assess the skills needed to pass this certification, so that every student/attendee is tested correctly and fairly.
Duration: 30 days
Pass: A pass is given once all the source code, testing and documentation has been assessed by our team.
Achievement: Certification (for life), with a digital certificate.
Module1: Introduction
Python primer
Python History
Why program in Python?
Uses of Python
Python setup
IDE setup: VSCode
IDE setup: PyCharm
Python internals
Built-in functions
PyPi
Working with pip
Python guidelines
Indenting
Commenting
Best practices
Pep8
Module 2: Basic building blocks
Basic data types
Python data types
Mutable vs Immutable
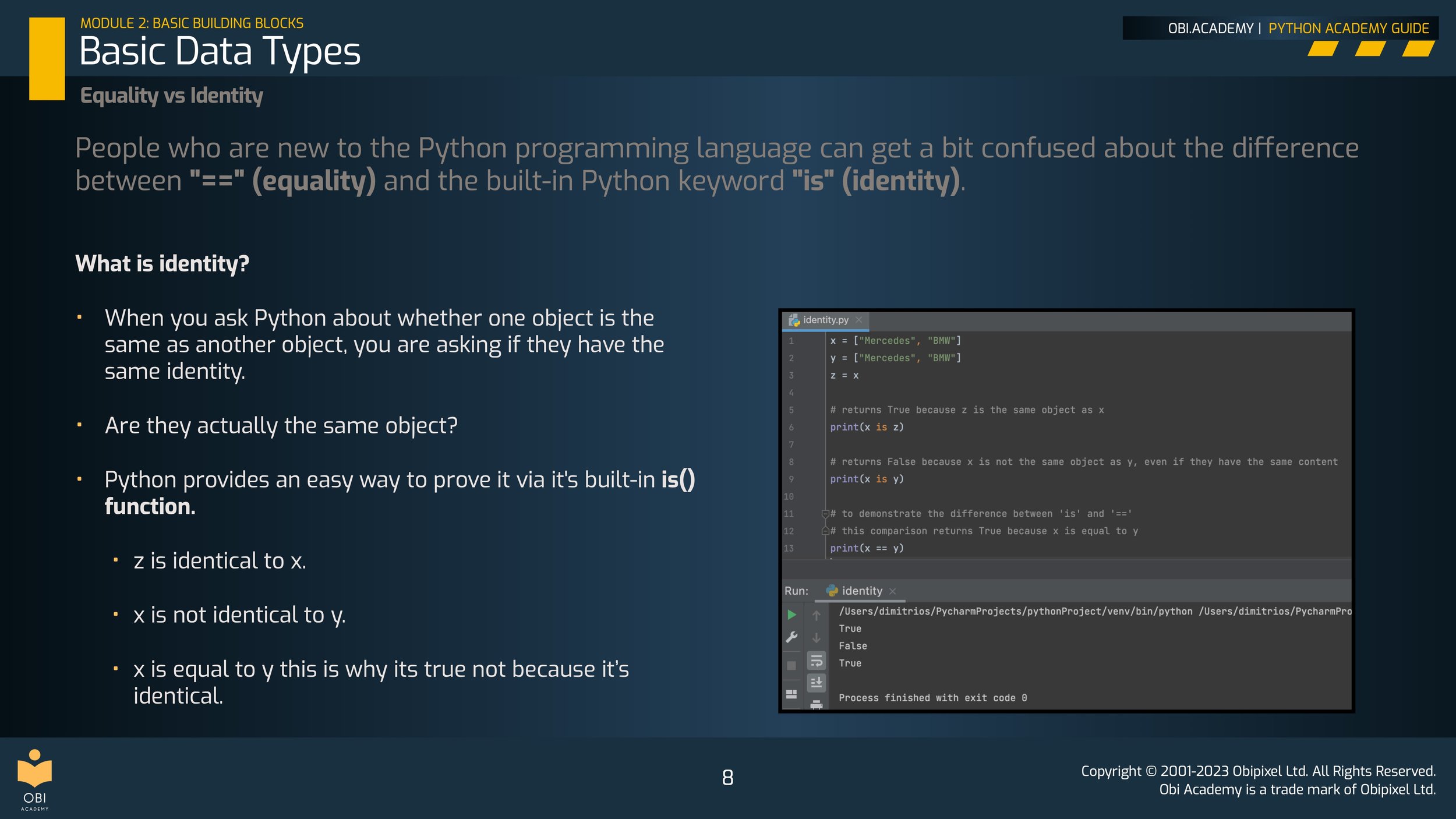
Equality vs Identity
Strings
Numbers
String Concatenation
String Concatenation with formatting
Variables
Variable basics
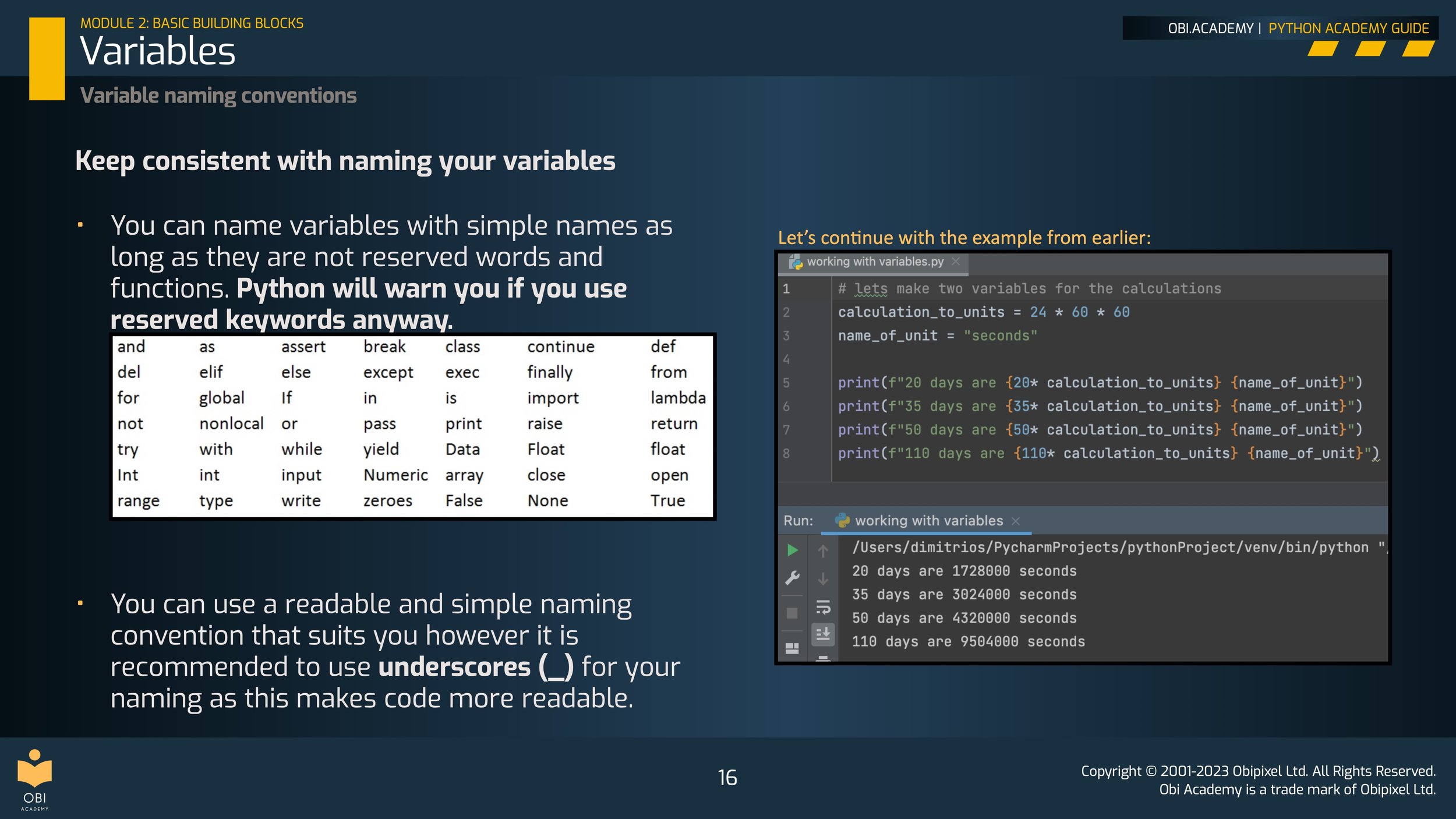
Variable naming conventions and reserved keywords/functions
Functions
Function basics
Function parameters
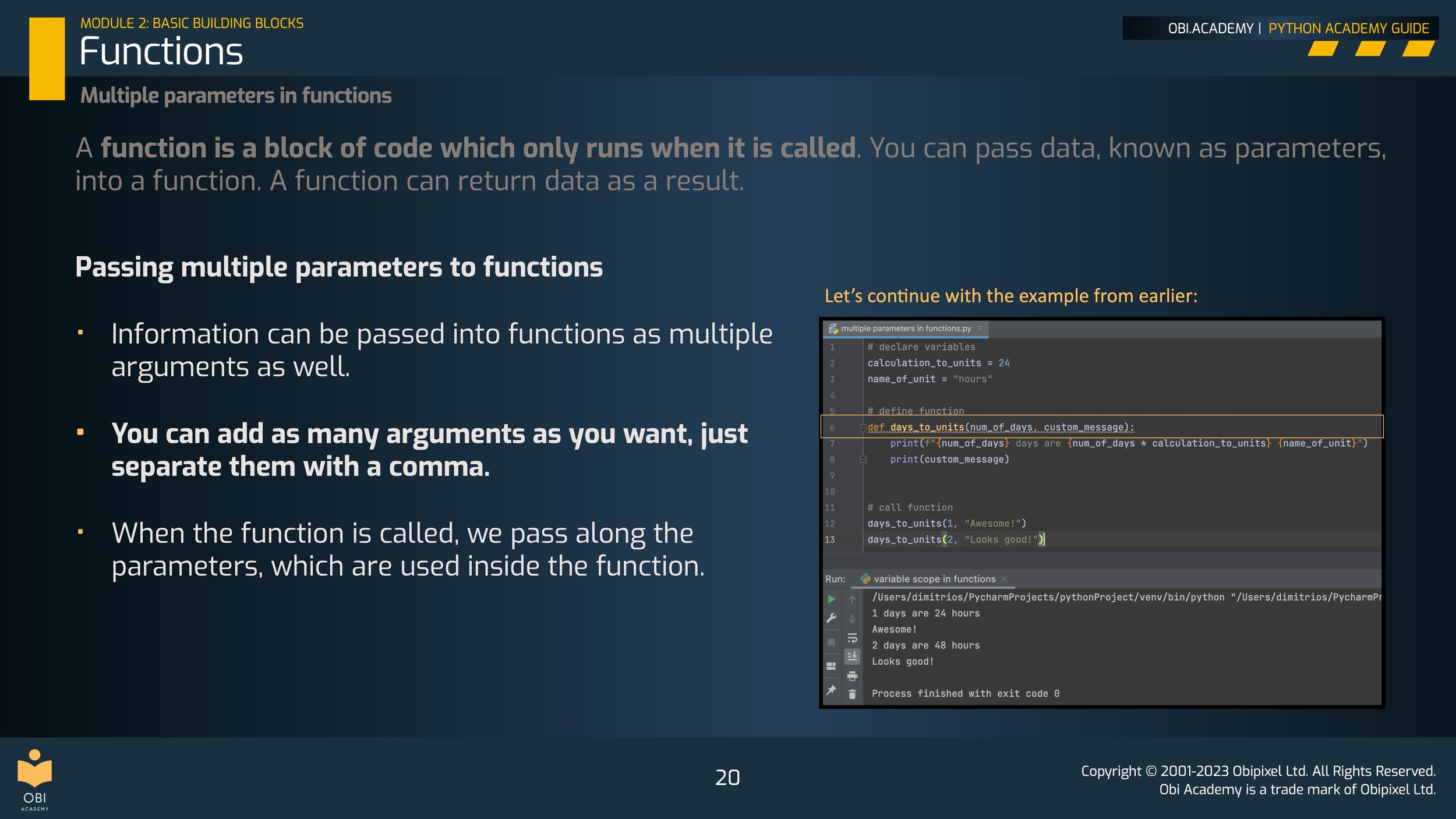
Multiple parameters in functions
Variable scopes in functions
Return value as parameter
User Input and Conditionals
User input basics
Accepting user input and casting
Conditionals (if/else) and Boolean data type
Checking for a negative value vs a zero value using conditionals (if, elif, else)
Dealing with data type conversions
Optimising code with multiple functions
Nested if/else
Try/Except and error handling
Loops and Lists
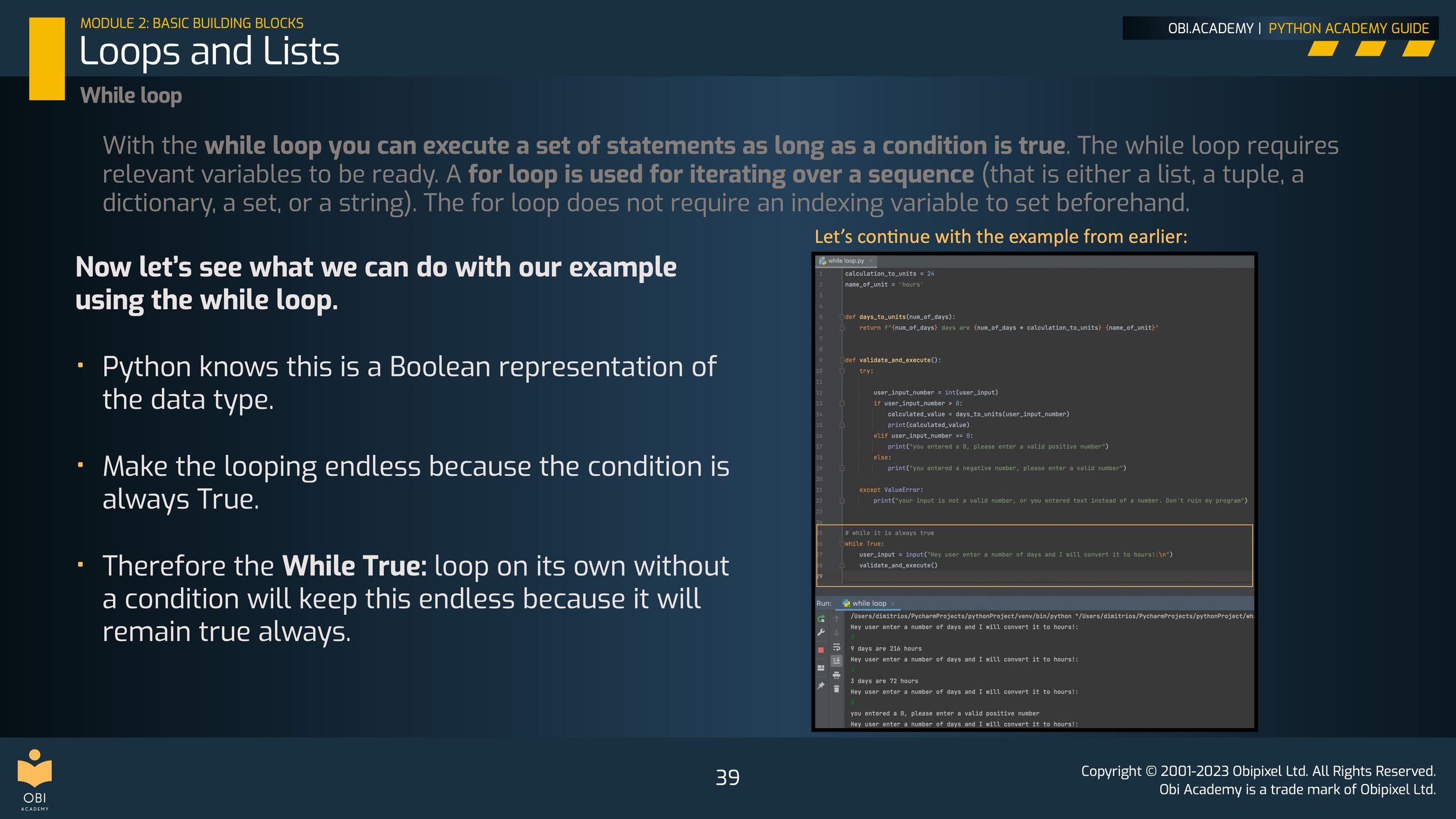
While Loop
Exiting loops
Basic list operations
Working with Lists and For loop
List comprehension
Sets and Dictionaries
Basics with Sets
Working with Sets
Basics of Dictionaries
Working with Dictionaries
Tuples
Introduction
Accessing Tuples
Updating Tuples
Unpacking Tuples
Looping Tuples
Modules
What are modules?
Working with modules
Importing built-in Python modules.
Built-in vs Third-Party modules.
Module 3: Object Oriented Programming
OOP Primer
Classes
Objects
Working with classes
Constructors
Inheritance
Property decorator
Module 4: Intermediate building blocks
Automation
Introduction
Working with automation
Iterators
Introduction
Working with iterators
Create an iterator
Stop an iterator
Generators
Introduction
Generator functions vs normal functions
Generator function
Generator object
Sequences
Introduction
Counting elements in a sequence
Checking if an item exists in a sequence
Finding the index of an item in a sequence
Slicing a sequence
Getting min and max items from a sequence
Concatenate sequences
Repeating a sequence
Working with files
Introduction
Opening files
Reading files
Writing/Creating files
Deleting files and folders
Encoding/Decoding
Introduction
Encode/Decode strings
Encode in Base64
Decode from Base64
RegEx
Introduction
RegEx functions
Using the findall() function
Using the search() function
Using the split() function
Using the sub() function
Using Metacharacters
Using Sets
Packages
Organising your code into packages
Generating numbers
Generating random numbers
Module 5: Working with data and APIs
Working with data
Managing data with databases
Working with databases and classes
Working with JSON
Data Analysis
Introduction
What is data cleaning?
Why is data cleaning important?
Data cleaning with the Pandas library
Standardising and normalising
Data Visualisation
Using matplotlib and plt
Plotting x and y points
Plotting without lines
Plotting multiple points
Default x-points
Creating bars
Bar colour
Horizontal bars
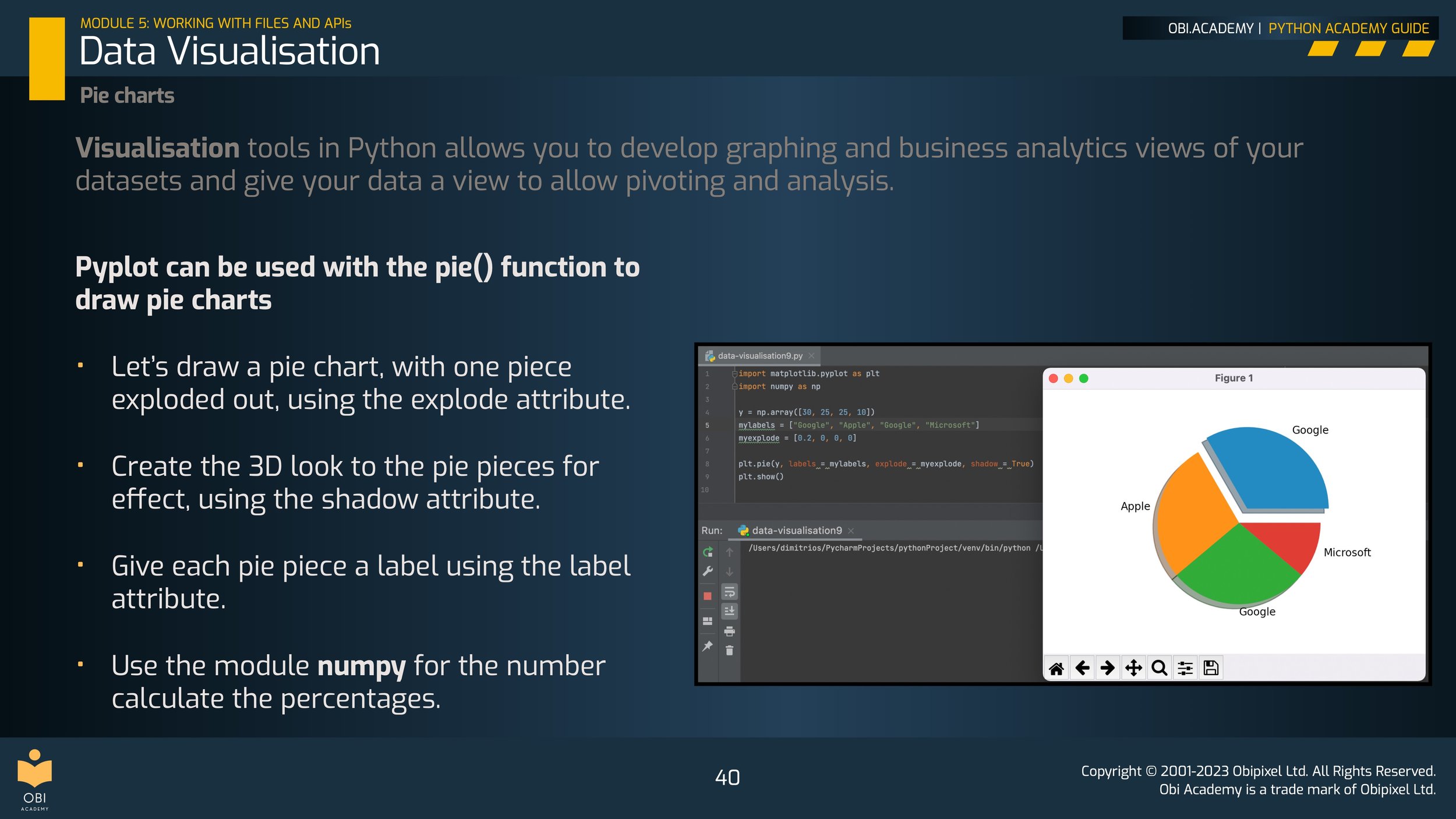
Pie charts
Data Transformation
Basic transform
Data frames
Transform
API
Introduction
Requests
Responses
Requests library
Synchronous requests
Asynchronous requests
Module 6: Networking Programming
Sockets and threading
Introduction
TCP sockets
UDP sockets
TCP socket flow
Socket programming
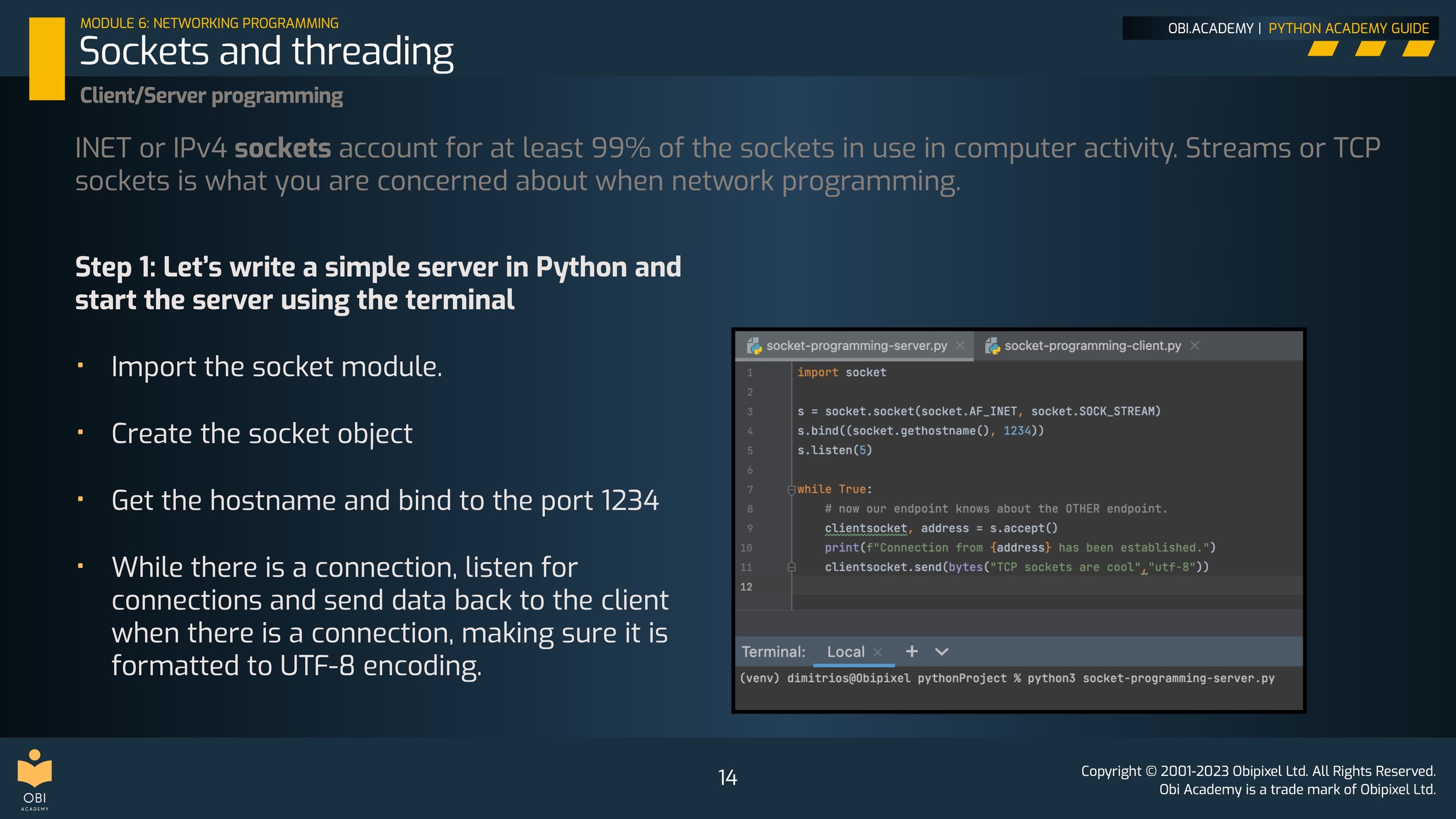
Client/Server programming
Threading
GIL Interpreter Lock
Module 7: Analysis, Code Management, Testing and Reporting
Analysis
Pylint
PyTest
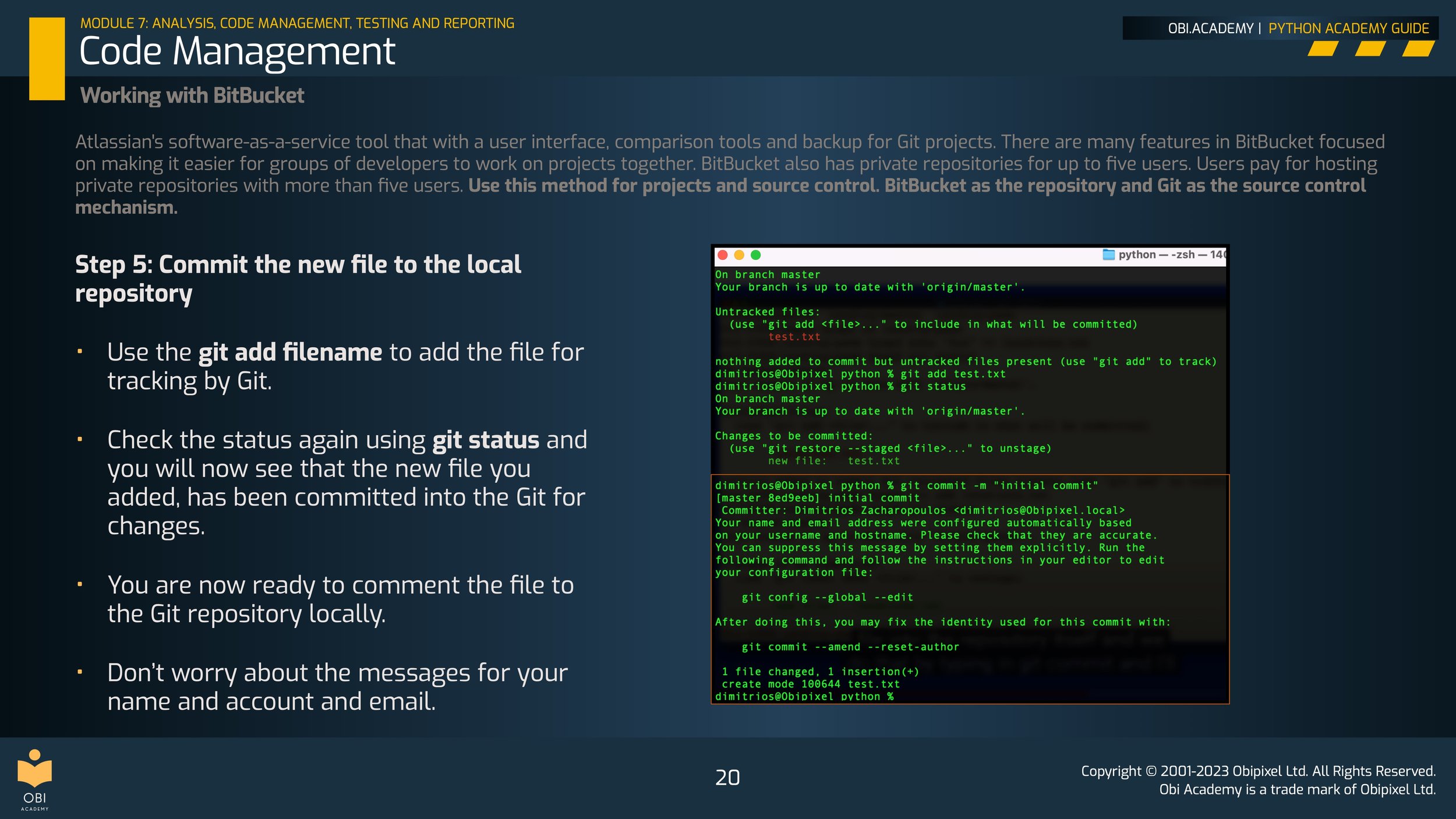
Code Management
Source control
Monorepo vs Multirepo
Source control during deployment
Source control projects
Documentation
Code review
Debugging code
Testing
Testing frameworks
Why Unit testing?
Unit testing with PyTest
Reporting
Reporting using HTML
Reporting using XLSX
Module 8: GUI Programming
TKinter
Introduction
Basics
Layout
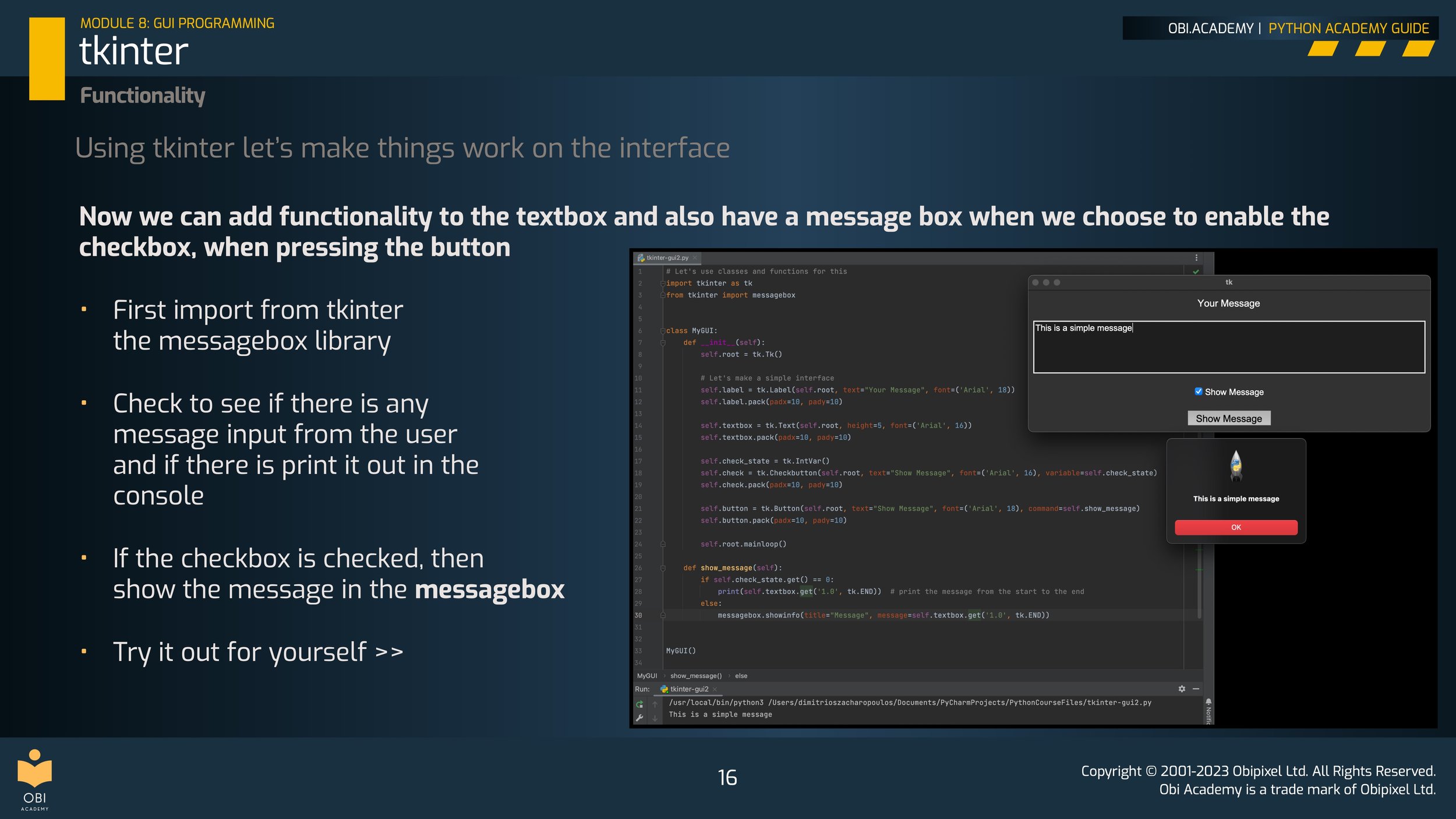
Functionality
Menus


